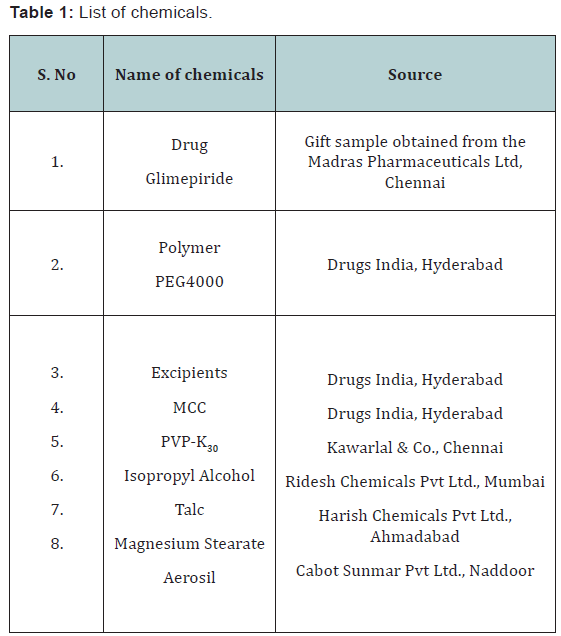
Formulation and Evaluation of Solid Dispersion of Glimepiride into Sustained Release-Juniper Publishers
JUNIPER PUBLISHERS-OPEN ACCESS GLOBAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES
A sustained release tablet containing Glimepiride was
formulated by using solid dispersion technique. Solid dispersions of
glimepiride were prepared by using Urea and PEG 6000 as carrier in drug:
carrier 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 1:4 ratios by Fusion method. From these all
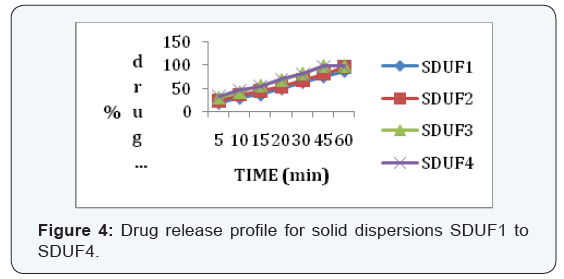
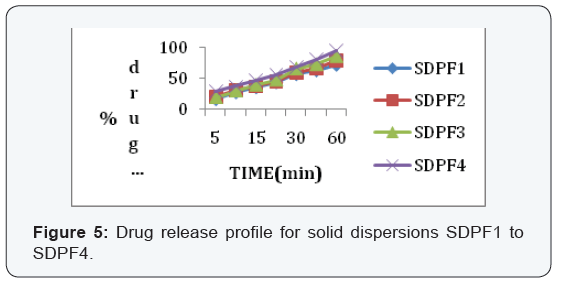
solid dispersions formulation SDUF3 containing Urea shows better
dissolution compared to other solid dispersions. This optimized solid
dispersion is formulated into sustained release tablets by direct
compression method using hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose and Ethyl
cellulose polymers.
Keywords: Solid dispersion, Diabetes mellitus, Sustained drug releaseAbbreviations: PVP: Poly Vinyl Pyrrolidone; HPMC: Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose; FTIR: Fourier Transform Infra Red; MCC: Micro Crystalline Cellulose
Introduction
The objective of sustained release [1] dosage form is
to preserve therapeutic blood or tissue levels of the drug for an
extended period. This is commonly accomplished by attempting to gain
zero order release [2] from the dosage form. Zero order release
establishes drug release from the dosage form that is autonomous of the
extent of drug in the delivery system (a constant release rate).
Sustained release system in general do not achieve this form of release
and regularly try to simulate Zero order release given that drug release
is in a slow first order manner (concentration dependent).Systems that
are selected as prolonged release can also be measured as efforts at
attaining sustained release delivery. Repeat-action tablets [3] are an
another techniques of sustained release in which several doses of the
drug are confined within a dosage system, and each dose is free at a
episodic interval. Delayed release system in difference, is usually not
sustaining. Generally, the release rate of drug is not changed and does
not effect in sustained delivery once drug release has commenced. The
word solid dispersion [4] denotes a group of solid products comprising
of a minimum two diverse constituents, largely a hydrophilic matrix and a
hydrophobic drug. The matrix can be any crystalline or amorphous. The
drug could be disseminated molecularly, either in amorphous state or in
crystalline state furthermore, it is the preparation method but not the
molecular arrangement which determines the properties of solid
dispersions.
Methods of Preparation of Solid Dispersions
Melting method
The melting or fusion method [5], comprises the
preparation water-soluble carrier and physical mixture of a drug and
then heating it directly until it reaches a melting point. Then in an
ice –bath with vigorous stirring the melted mixture is solidified. Then
in the final stage the solid mass is crushed, pulverized and sieved.
Solvent method
In the solvent method [6], in a common solvent the
physical mixture of the drug and the carrier are mixed together, and
then evaporated till a clear, solvent free film is left. Then the film
is additionally dried to constant weight.
a. Diabetes mellitus: [7] or only
diabetes, is defined as where a person has high blood sugar, either the
cells do not respond to the insulin, or the pancreas do not produce
enough insulin.. This high blood sugar is characterised by polyuria
(frequent urination), polydipsia (increased thirst) and polyphagia
(increased hunger) [8].
b. Type 1 diabetes: mellitus [9] is
described as loss of the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas,
which leads to insulin deficiency. The common of type 1 diabetes is of
immune-mediated nature, where beta cell loss is mediated by T-cell
autoimmune attack. There is no certain precautionary measure against
type 1 diabetes, which is responsible for 10% of diabetes mellitus cases
in North America and Europe. When onset occurs affected people
are healthy and with healthy weight. In the early stages sensitivity
and responsiveness to insulin are generally normal.
c. Type 2 diabetes: Type 2 diabetes mellitus [10] is described
as resistance to insulin where it is combined with fairly decreased
insulin secretion. This is said to involve the insulin receptor. This
is the most common of types.
d. Gestational diabetes: Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)
[11] bear a resemblance to in most of the aspects, with decreased
insulin secretion and its response. It is seen in 2-3% of pregnancies
and it may improve or disappear after pregnancy which is
completely treatable. This may require medical observation
during the pregnancy period.
e. Other types: Prediabetes [12]. Is a state where the person’s
glucose levels are higher than the normal but cannot be diagnosed
for type 2diabetes? Persons who develop diabetes type 2 spend
most of their years in Prediabetes state which is termed as
“America’s largest healthcare epidemic” [13]. Latent autoimmune
diabetes of adults (LADA) [14] is a condition which develops in
adults and is of type 1. The aim of the present investigation was
to develop and evaluate a direct compressed sustained release
tablets developed by solid dispersion technique. The tablet
investigated in the current study consists hydroxyl propyl methyl
cellulose which helps in the sustained release of the tablet. Solid
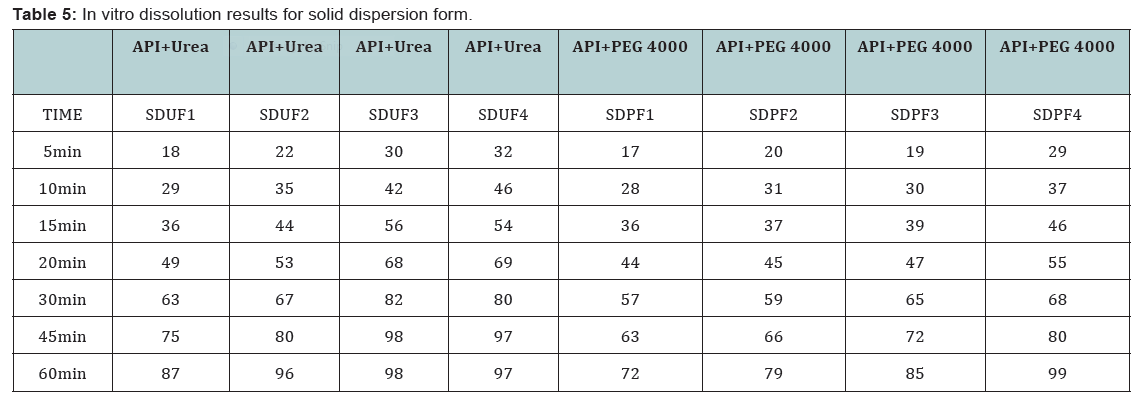
dispersion prepared by using urea showed better dissolution rate
than with PEG6000 (Table 1&2).
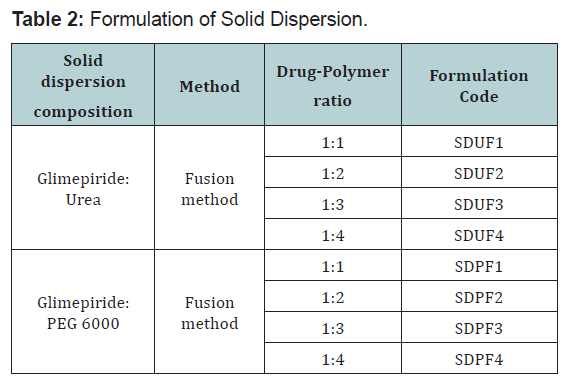
Physical mixture of Glimepiride with the combination of PEG
6000 was prepared thoroughly by mixing the accurately weighed
amount of drug and polymer in glass motor and pestle for 5
minutes and sieved through 0.25mm sieve (#60) and stored in
desiccators for 24hours for further studies.
Preparation of solid dispersion by fusion method
Physical mixtures were melting in water bath with gradual
increasing temperature up to the value necessary for the
complete melting. The molten mass was rapidly cooled with
constant stirring with a glass rod. The resulting solid dispersion
was stored in desiccators for 24hrs,after then the prepared solid
dispersion was grounded in motor for 2min ,and passed through
0.25(#60) mesh and used for further studies. Solid dispersion
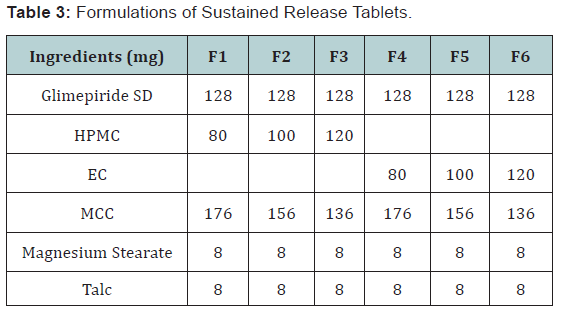
into sustained release Glimepiride tablet is prepared through
wet granulation method [7] accordingly. Steps like sieving, dry
mixing, preparation of binder solution, granulation and drying are
involved. This preparation was passed through no.20 sieve. Solid
dispersion of glimepiride, HPMC, Ethyl cellulose and MCC were
mixed thoroughly in a poly bag to ensure uniform mixing with the
drug for 5 minutes. 9mg of PV K-30 is weighed accurately and then
mixed with IPA to form a binder solution which was added slowly
to the dry mix to form uniform granules. The wet granules are
then dried by air drying as IPA is corrosive and gets evaporated
quickly. The dried samples are removed at random at regular time
intervals and then passed through sieve no.20 and lubrication was
done (Table 3).
Results and Discussion
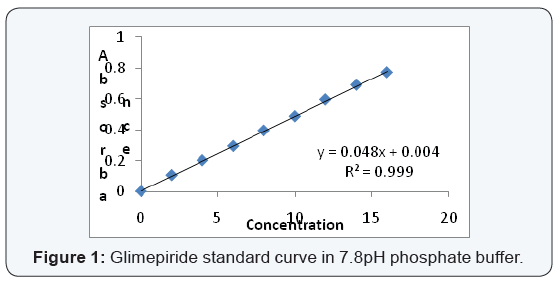
Analytical methods
From the standard stock solution (1000 μg/ml), appropriate
aliquot were transferred to series of 10 ml volumetric flasks and
made up to 10 ml with desired solvents so as to get concentration
of 5,10,15,20… or 2,4,6,8… μg/ml. the absorbance of the solution
were measured at 230 nm for Glimepiride. This procedure was
performed in triplicate to validate calibration curve and a graph
is plotted (Figure 1).
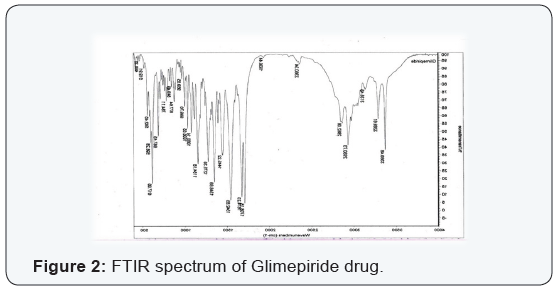
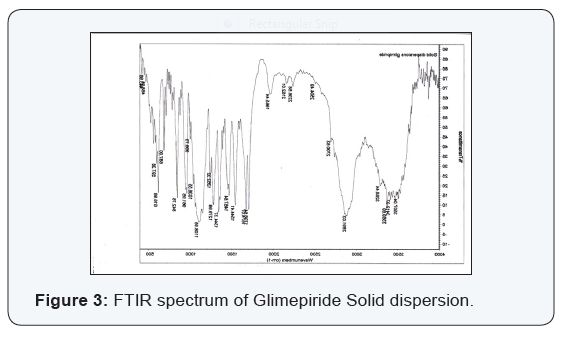
Compatibility studies
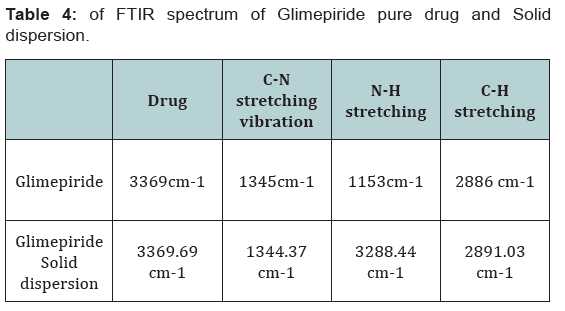
FT-IR spectroscopy is employed to establish the compatibility
of drug with polymer and individual drug. Both the spectra were
compared for confirmation of common peaks. Glimepiride with
polymers showed no significant variation in height, intensity
and position of peaks, suggesting that drug and recipients were
compatible. Interaction between drug and polymer has not been
established. Hence it can be determined that the drug is in Free
State and can be released easily (Figure 2-11), (Tables 4-7).
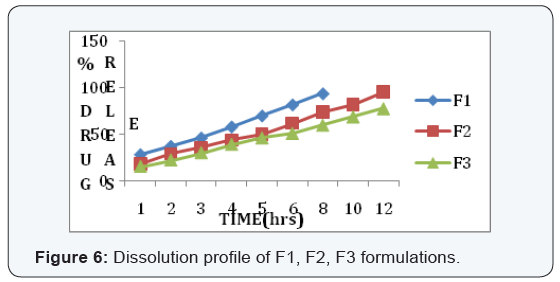
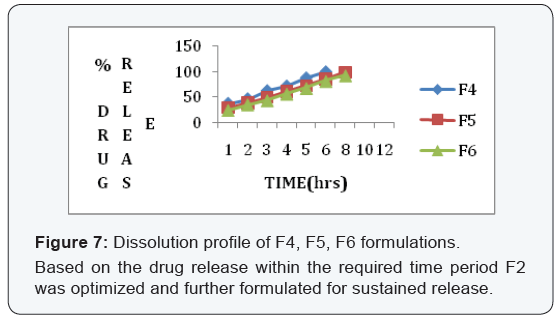
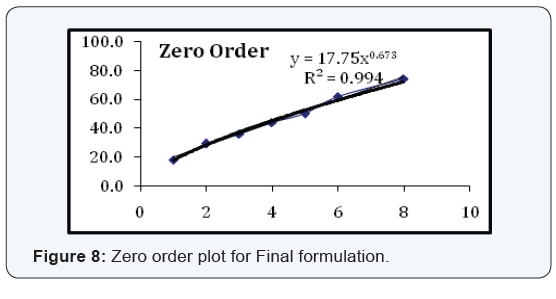
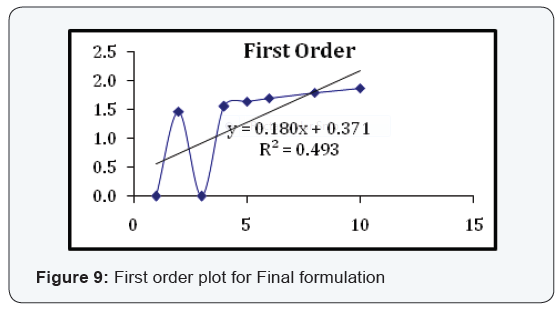
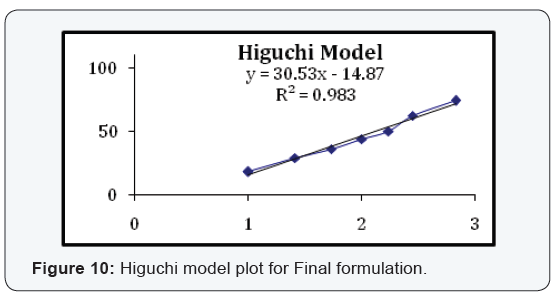
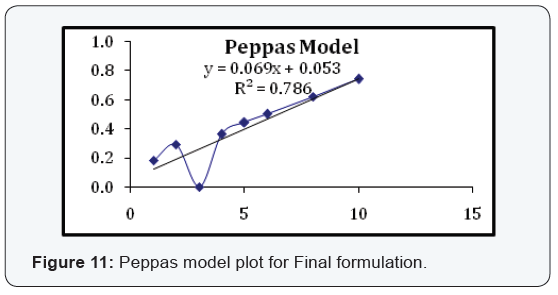
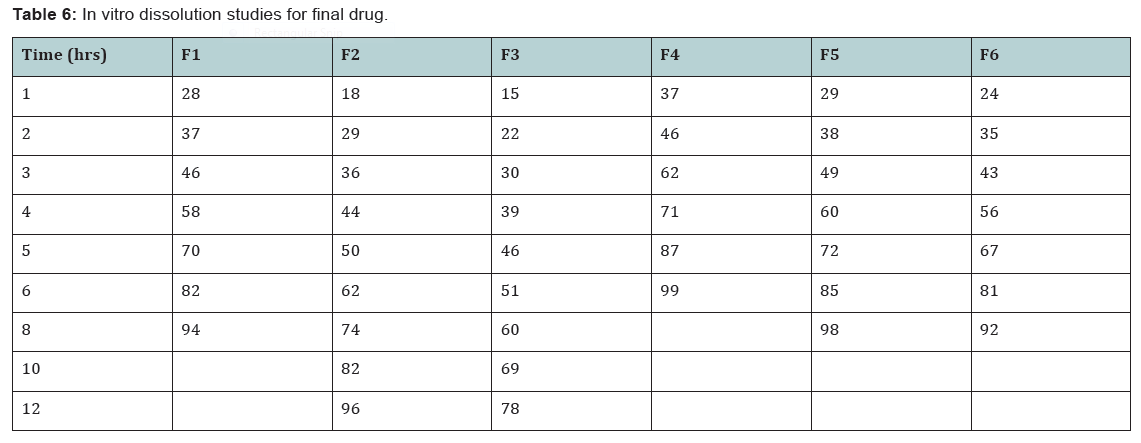
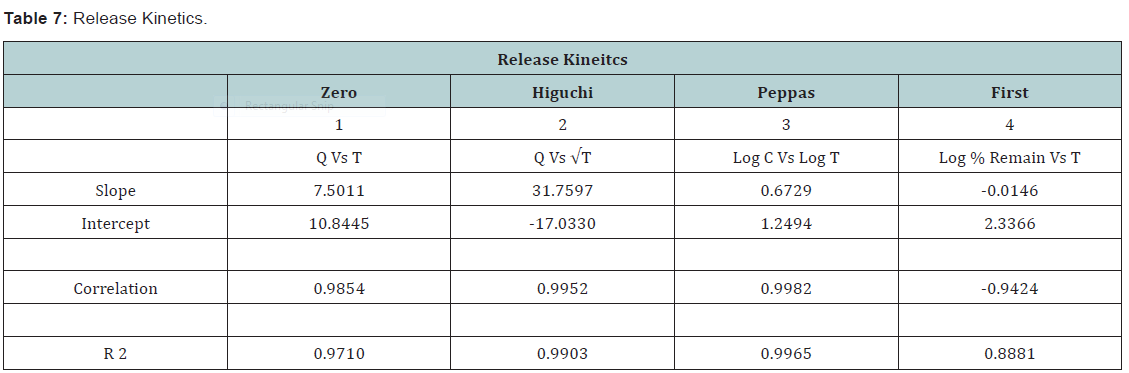
Conclusion
In the 6 trials, the optimized formulation was F2 which
releases the drug Glimepiride in a sustained fashion up to 12
hours with96% of drug release.
For more articles in Global Journal of Pharmacy
& Pharmaceutical Sciences please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/gjpps/index.php
To know more about Juniper Publishers please click on: https://juniperpublishers.business.site/



Comments
Post a Comment